Microservices Architecture: A Beginner’s Guide
Microservices architecture has become a popular approach for building complex, scalable applications. In this post, we’ll explore the fundamental principles, common patterns, and practical strategies for implementing microservices effectively.
What Are Microservices?
Microservices architecture involves designing an application as a collection of small, independent services, each responsible for a specific function. These services communicate with each other through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces).
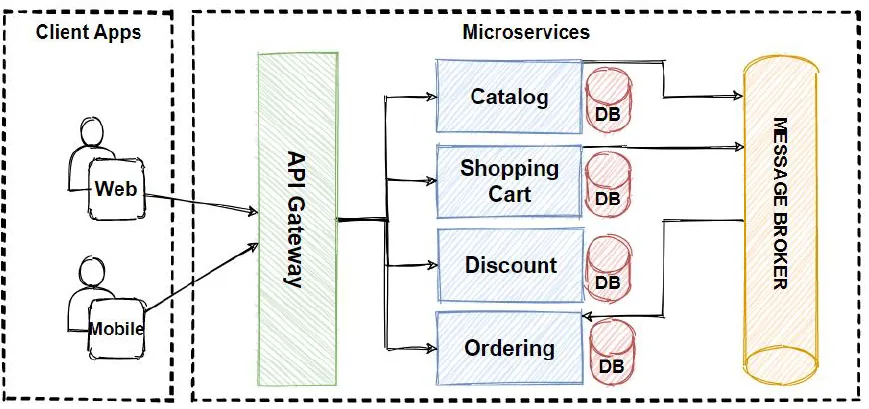
Key Features of Microservices:
- Single Responsibility: Each service focuses on one task, such as handling payments or managing users.
- Independent Deployment: Services can be developed and deployed independently without affecting the entire system.
- Technology Diversity: Different technologies can be used for different services, allowing teams to choose the best tools for each function.
- Scalability: Services can be scaled individually, improving resource utilization and system performance.
This contrasts with the traditional monolithic architecture, where all components are combined into a single system.
Principles of Microservices
Several principles guide the design of microservices:
1. Single Responsibility
Each microservice should focus on a specific business function. For example, in an e-commerce application, separate services might handle orders, customers, and payments.
2. Independence
Microservices should be developed, deployed, and updated independently. This allows for faster development cycles and reduces the risk of system-wide failures.
3. Domain-Driven Design
Microservices should be designed around business domains rather than technical layers. This approach ensures that each service aligns with business capabilities.
Common Microservices Patterns
Implementing microservices effectively involves using certain architectural patterns:
1. API Gateway
An API Gateway acts as a single entry point for all clients, routing requests to the appropriate microservices. This simplifies client interactions and can handle concerns like authentication and rate limiting.
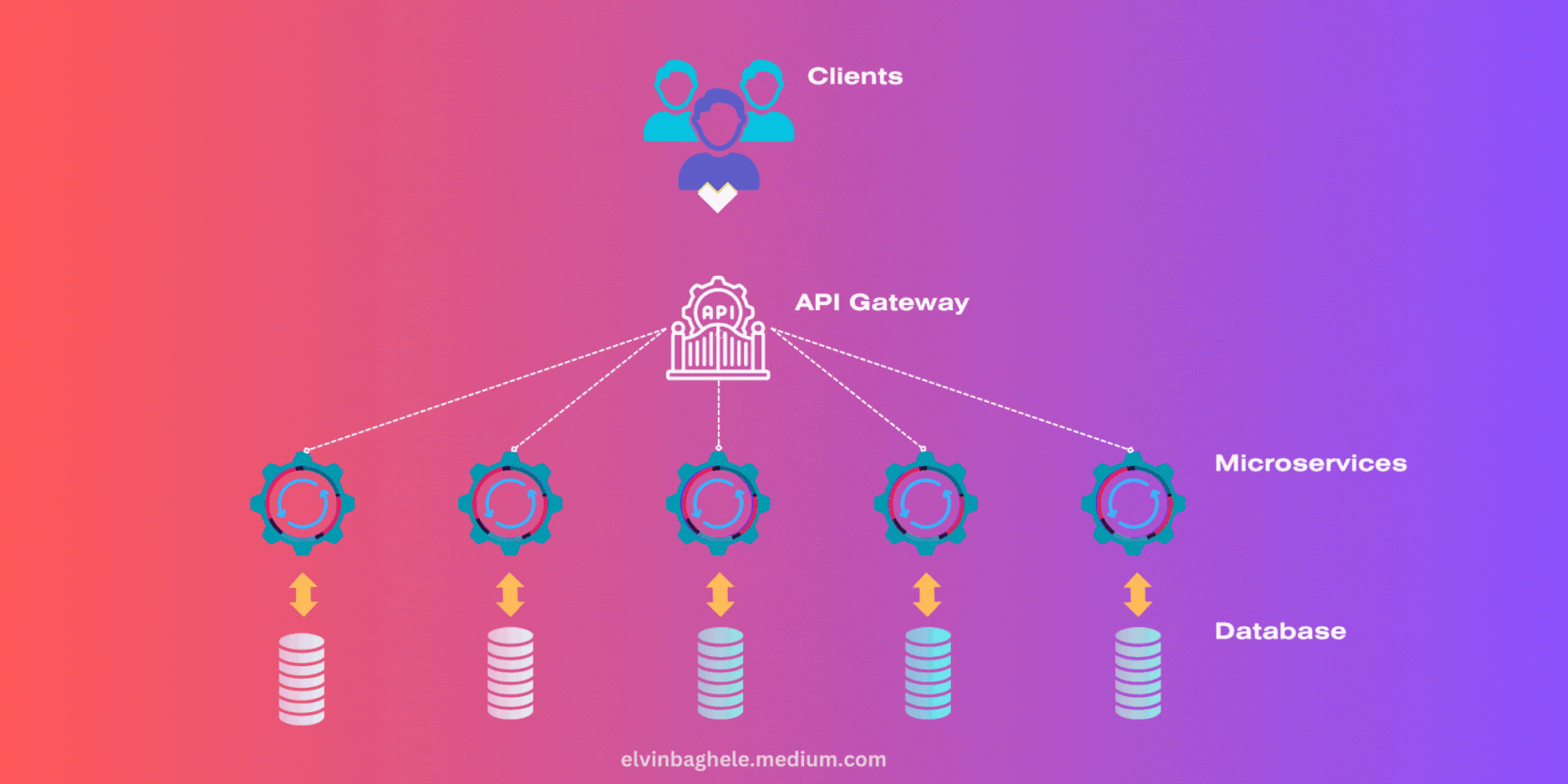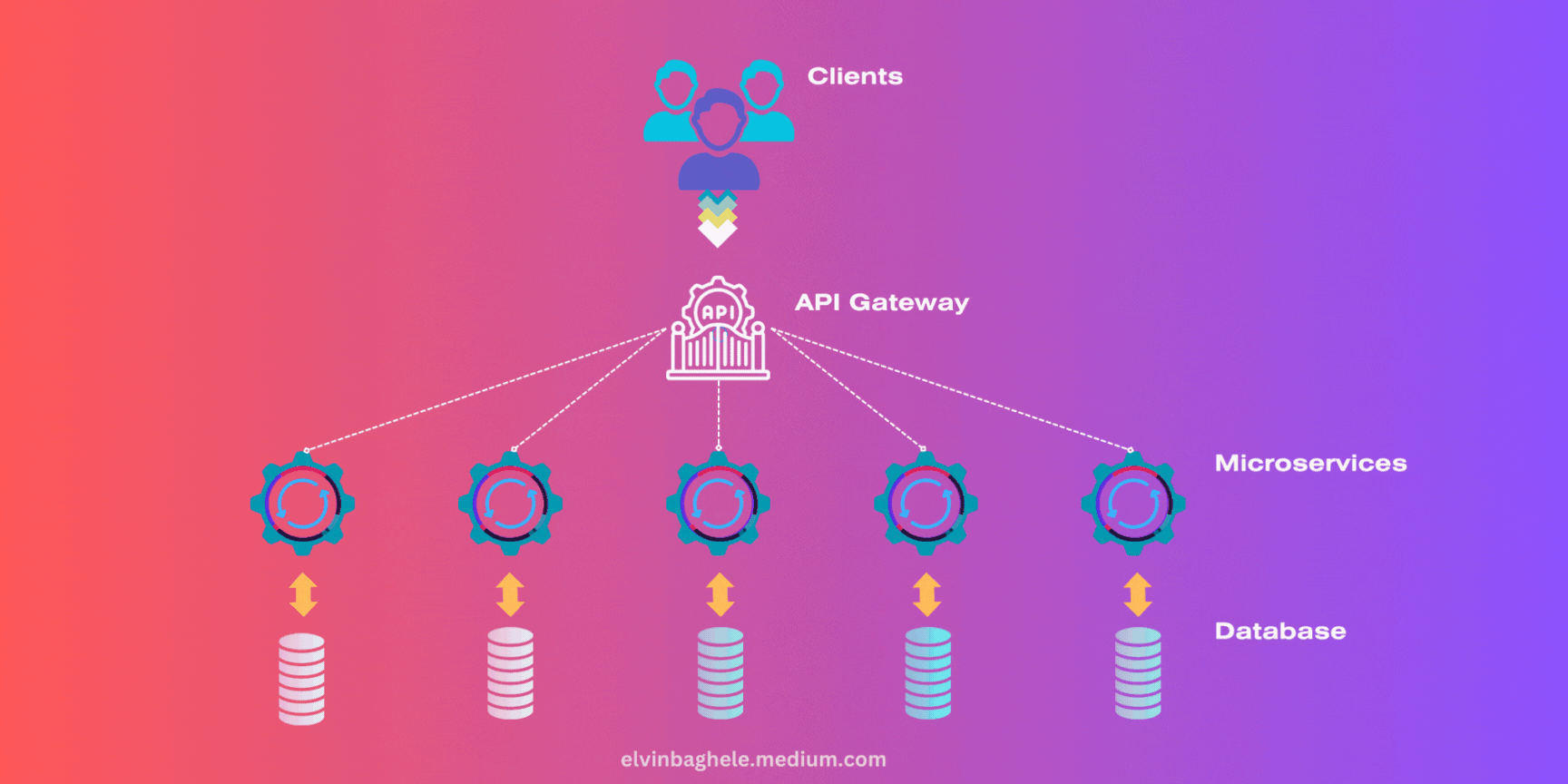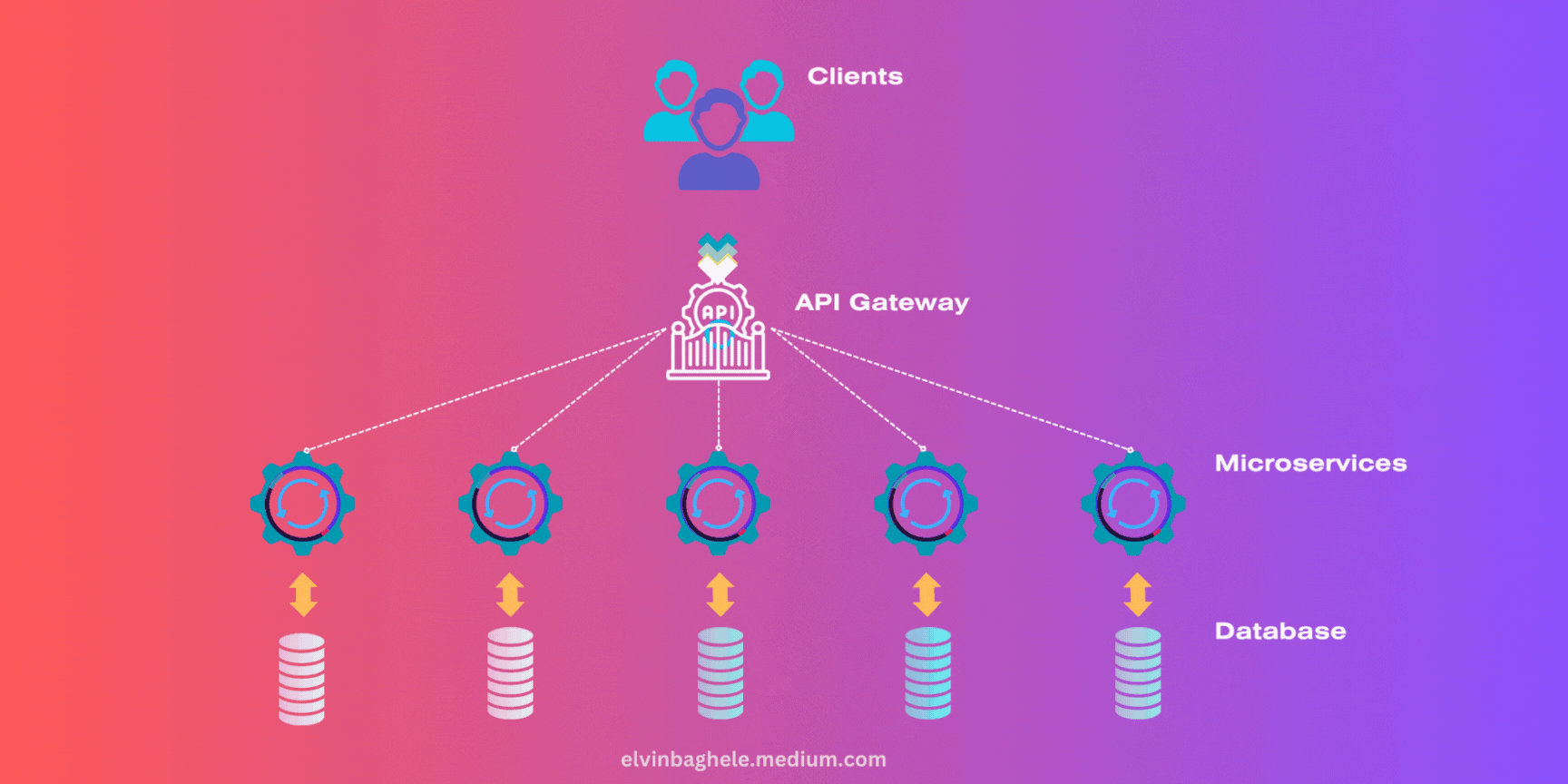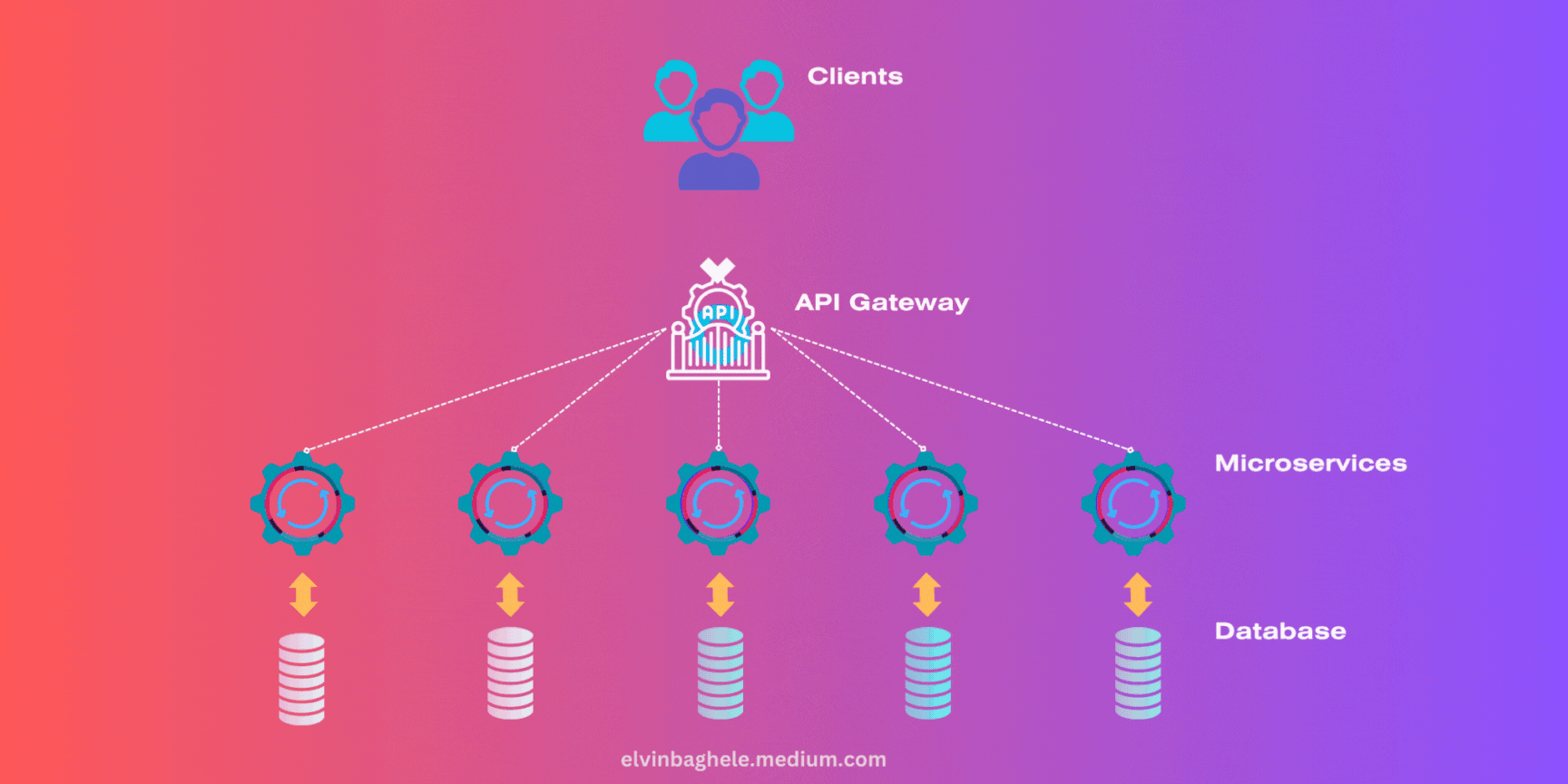
2. Circuit Breaker
The Circuit Breaker pattern prevents a service from repeatedly trying to execute an operation that’s likely to fail, helping to maintain system stability.
public class CircuitBreaker {
private boolean isOpen = false;
private int failureCount = 0;
private final int failureThreshold = 3;
public void callService() {
if (isOpen) {
System.out.println("Circuit is open. Failing fast.");
return;
}
try {
// Call to external service
// simulateServiceCall();
failureCount = 0; // Reset on success
} catch (Exception e) {
failureCount++;
if (failureCount >= failureThreshold) {
isOpen = true;
// Schedule reset of circuit after some time
}
}
}
}
3. Event-Driven Communication
Services communicate asynchronously through events, enhancing scalability and decoupling.
Challenges of Microservices
While microservices offer many benefits, they also present certain challenges:
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Managing multiple services increases system complexity. | Use orchestration tools like Kubernetes. |
| Data Consistency | Ensuring data consistency across services is challenging. | Implement eventual consistency where feasible. |
| Inter-Service Communication | Services need efficient communication mechanisms. | Use lightweight protocols like HTTP/REST or messaging queues. |
When to Use Microservices
Microservices are suitable when:
- The application has distinct, separable business functions.
- Independent scaling of components is required.
- Teams are organized around business capabilities.
However, for small applications, a monolithic approach might be more straightforward.
Conclusion
Microservices architecture offers a modular approach to building applications, promoting scalability and flexibility. By understanding its principles and patterns, developers can design systems that are resilient and adaptable to changing business needs.
For a more in-depth understanding, you might find this video tutorial helpful:
[
Video: Microservices Explained: A Beginner's Guide
